Search in this section
Instructions for the complete automation of the registration of a domain, using the example of the domain example.com.
.com is a generic top-level domain, which is well suited for the first implementation due to the lack of restrictions.
Basics of the JSON and XML API
All important information for the use of the JSON and XML API you can find in the General API Basics and the XML API Basics and JSON API Basics.
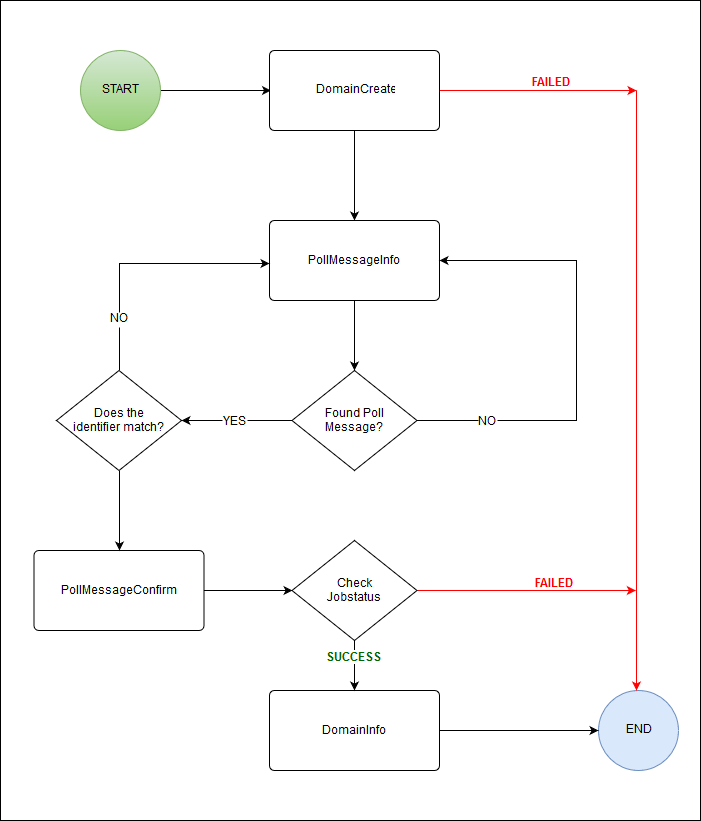
Process overview
Flow chart
Task names, codes and routes
| Task | Code | Route |
|---|---|---|
| ContactCreate | 0301 | POST /contact |
| DomainCreate | 0101 | POST /domain |
| PollInfo | 0905 | GET /poll |
| PollConfirm | 0906 | PUT /poll/$id |
| DomainInfo | 0105 | GET / domain/$name |
Requirements
Domain contacts
To order a .com domain you need a domain owner (OwnerC), an administrative contact (AdminC) and a technical contact (TechC). You can use existing contacts or create new ones.
Contact create - example
Process
Registering domains is an asynchronous process because the registry is involved in the processing of the order. The system notifications are provided in the system upon receipt and can be retrieved by polling.
For more details on asynchronous notifications, see page Asynchronous Notifications.
Starting a domain create request
With the request type DomainCreate you start the registration of the domain. The following values are required:
- Contacts: The contact ID of the required contacts. For .com domains, a domain owner, an administrative contact and a technical contact are required.
- Domain: The name of the domain
- Name server: The desired name servers. The number of name servers required depends on the TLD.
Which additional data is required for a domain depends on the TLD. Each registry has its own guidelines. Further information can be found in the TLD Knowledge Base.
Domain create - Example
Receiving notifications
The DomainCancelationCreate task creates a cancelation request. This triggers the creation of a second cancelation request, which is processed later at the time defined in the request (=asynchronous processing).
Once this second request has been processed, a system notification is generated, indicating whether the deletion was successful or not. The notification can be retrieved using the Polling and Push methods.
Inquiring domain data
After successful registration, you can query the registration data stored in the system with the DomainInfo task. This enables you to determine whether the domain has been registered with the desired data.